T Slot Cutting On Milling Machine Lab Manual
In reference to milling machines, the distance, measured in feet or meters, that a point on the cutter's circumference will move in one minute. In reference to lathes, the distance the work moves past the cutting tool, expressed in feet per minute or meters per minute. Measuring is done on the circumference of the work.
21.02.2020 by Andreas VellingCNC machining is a highly utilised subtractive manufacturing technology. Computer numerical control systems offer less need for manpower and higher levels of automation.
One of these automated fabrication methods is CNC milling. It is a process where rotary cutters remove material, which makes it the opposite of CNC turning.
The milling centres do not just perform the cutting automatically, but also the changing of tools. During the average process of creating a finished product from a block of metal, for example, various tools are used.
So let’s see what milling tools are used on the machines and what are the purposes of each.
What Are the Types of Milling Cutters?
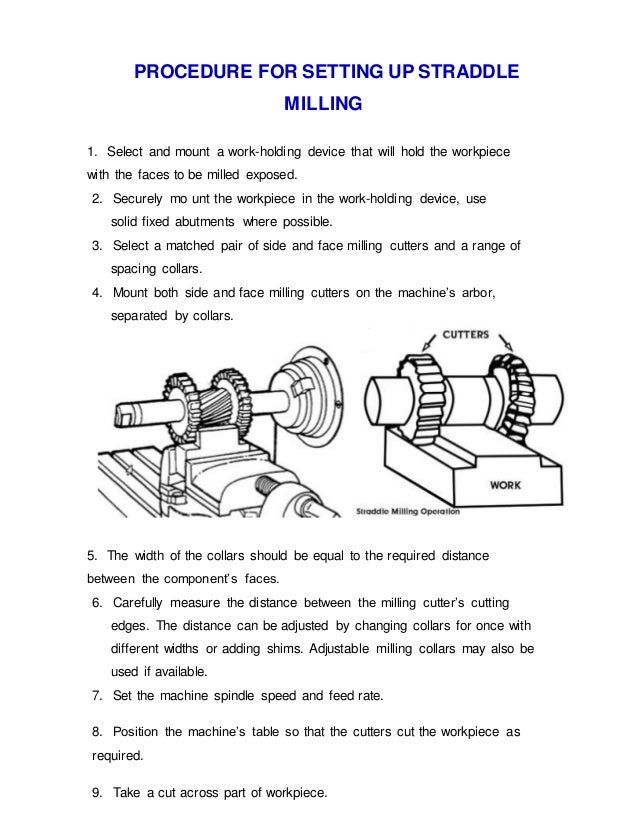
Contour milling, shallow slotting, contour milling and pocketing applications. Flutes Spiral-shaped cutting edges are cut into the side of the end mill to provide a path for chips to escape when an end mill is down in a slot or a pocket. The most common options are 2, 3, or 4 flutes. The more flutes, the more cutting edges but the. Up Cut Milling In up cut milling, the cutter rotates in a direction opposite to the table feed as illustrated in figure 14. It is conventionally used in most milling operations because the backlash between the leadscrew and the nut of the machine table can be eliminated. Up Cut Milling b. Down Cut Milling. Illustrates gear cutting milling operation. Spur, helical gears are cut on a milling machine with the help of an indexing mechanism. The operation of gear cutting is cutting of equally spaced, identical gear teeth on a gear blank by handling it on a universal dividing head and then indexing it.
The most common types of milling cutters are:
- End mill
- Face mill
- Ball cutter
- Slab mill
- Side-and-face cutter
- Involute gear cutter
- Fly cutter
- Hollow mill
- Shell mill
- Roughing end mill
- Dovetail cutter
- Wood ruff cutter
First, we should start with one of the primary questions.
What is the difference between end milling and face milling?
These are two of the most prevalent milling operations, each using different types of cutters – the and mill and the face mill. The difference between end milling and face milling is that an end mill uses both the end and the sides of the cutter, whereas face milling is used for horizontal cutting.
End mill
These tools usually have a flat bottom but not always. Round and radiused cutters are also available. End mills are similar to drills in the sense that they can cut axially. But the advantage for milling lies with the possibility of lateral cutting.
Face mill
Face mills cannot cut axially. Instead, the cutting edges are always located on the sides of the cutting head. The cutting teeth are replaceable carbide inserts.
This makes the lifetime of a tool longer while maintaining a good cutting quality.
Ball cutter
Ball cutters, also known as ball mills, have a hemispherical cutting tip. The objective is to maintain a corner radius for perpendicular faces.
Slab mill
Slab mills are not that common with modern machining centres. Rather, they are still used with manual milling machines to quickly machine large surfaces. That is also why slab milling is often called surface milling.
The slab itself spins in a horizontal position between the spindle and the support.
Side-and-face cutter
A predecessor for the end mill. Side-and-face cutters have teeth around the circumference as well as on one side. This makes the functionality very similar to end mills but their popularity has waned over the years with the advancement of other technologies.
Involute gear cutter

There is a special cutting tool for milling involute gears. There are different cutters available to produce gears within a certain number of teeth.
Fly cutter
These tools have the same function as face mills. They consist of a central body that holds either one or two tool bits (double-end fly cutters).
Face mills are better for high quality cutting. Fly cutters are just cheaper and the cutting bits are often made at the shop by a machinist rather than bought from stores.
Hollow mill
Hollow mills are basically the opposite of face mills. Here, the workpiece is fed into the inner part of the mill to produce a cylindrical outcome.
Roughing end mill
As the name says, these are pretty much end mills with a slight difference. The roughing end mill has jagged teeth. These make the cutting process faster than with a regular end mill.
The cut bits of metal are smaller than usual and therefore easier to clear. Multiple teeth come into contact with the workpiece at the same time. This reduces chatter and vibration, which could otherwise be larger because of the jagged teeth.
Woodruff cutter
Woodruff, or keyseat/keyway cutters are used to cut keyslots into parts, for example shafts. The cutting tools have teeth perpendicular to the outside diameter to produce suitable slots for woodruff keys.
Thread mill
The name of this tool says everything you need to know about its purpose. Thread mills are used for producing tapped holes.
Threading operations are usually carried out on drilling equipment. Using a thread mill, though, is more stable and has less limitations regarding the environment.
What Materials Are Used for Cutting Tools?
As you could see, there are a lot of different machine tools available for wide range of purposes. The same applies to the materials used to make these tools.
Let’s dig deeper to look at the most common materials for milling bits.
Carbon steel
Milling Machine Definition

The cheapest of the bunch. And this is exactly why it still finds use. As carbon steel is not very durable, it is only suitable for low-speed operations.
T Slot Cutting On Milling Machine Lab Manual 2017
Carbon steel loses its hardness at 200° C. This is the reason for lower speeds – to keep the heating effect low.
High-speed steel
High-speed steel, a grade of tool steels, has a few alloying elements added to it to provide better response to heat and wear than a regular carbon steel. While the life cycle of such a tool goes up, so does the cost.
Loses its hardness at 600° C. Therefore, higher milling speeds are suitable for these tool steels.
Cemented carbides
This material is harder than high-speed steel but the toughness qualities are not that impressive. The higher hardness provides better protection against wear but lower toughness levels make it a little more susceptible to cracking and chipping.
The upper temperature of use is at 900° C.
Cutting ceramic
Cutting ceramics are even harder than cemented carbides but lose in the toughness aspect. Both aluminium oxide and silicon nitride are used to produce these tools with varying properties.
Cutting ceramic tools are prone to cracking when used on hard materials and with high temperatures. Therefore, they are not really suitable for machining steels, for example. Otherwise a short tool life is to be expected.
Selecting the Right Machine Tool
As is the norm in manufacturing, the choice of method or tool comes down to a balance between speed, cost and quality. The cost depends on both the price of the tool, the wear machining results in, and the time it takes (speed) to produce the parts.
Choosing the material of the tool
Regular carbon steels are usually out of the option pool because of their limited capabilities. HSS (high-speed steel) is therefore the most inexpensive one to get the job done. At the same time, its rate of wear means that in the long run, there are better options.
Cobalt-bearing HSS, for example, are suitable for even quicker milling. This makes them sufficiently adequate for most jobs.
Cemented carbide is another step towards high performance milling because of the aforementioned properties of such milling machine tools. In the long run, they are a more cost-efficient choice while the up-front costs are higher.
Diameter
This is quite simple. A tool with a large diameter is able to mill the part quicker. Limitations apply based on the geometry of the final part.
For example, if certain inside radii are necessary, the tool cannot deviate from them. At the same time, you can use a large tool for milling away the bulk of it and apply a smaller one to finish the inside corners.
Tool coating
There are some different coatings available to protect the tools from wear. For example, a titanium nitride coating increases the tool’s lifespan but also the cost of it.
Such a coating reduces stickiness of the cutting material which can be a problem with aluminium. Therefore, less lubricant is necessary during the cutting process.
Number of flutes
Flutes are the channels on a milling bit. More flutes allow a higher feed rate because less material is removed.
T Slot Cutting On Milling Machine Lab Manual Download

At the same time, this increases the overall diameter of the milling cutter. This leaves less room for swarf.
Angle of helix
The helix angle, along with the rotation speed of the spindle, determines the cutting speed or feed rate. A steeper angle is suitable for softer materials and metals.
Choosing the right milling cutters for your job needs an understanding of the materials, parameters and definitely some experience. The final outcome depends on these choices and a machinist must understand what material cutters are suitable for cutting different mediums.
A good choice leads to high feed rates and therefore shorter cutting times as well as lower costs.
T Slot Cutting On Milling Machine Lab Manual Free
When choosing a CNC machining service, make sure that they have all the necessary tools to make your parts.